|
Size: 172
Comment:
|
Size: 1288
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 6: | Line 6: |
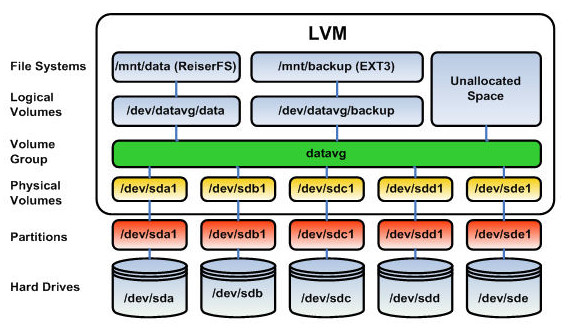
| = Item 1 = | = Description = In Linux, Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a device mapper target that provides logical volume management for the Linux kernel. LVM is used for the following purposes: * Creating single logical volumes of multiple physical volumes or entire hard disks (somewhat similar to RAID 0, but more similar to JBOD), allowing for dynamic volume resizing. * Managing large hard disk farms by allowing disks to be added and replaced without downtime or service disruption, in combination with hot swapping. * On small systems (like a desktop), instead of having to estimate at installation time how big a partition might need to be, LVM allows filesystems to be easily resized as needed. * Performing consistent backups by taking snapshots of the logical volumes. * Encrypting multiple physical partitions with one password. LVM can be considered as a thin software layer on top of the hard disks and partitions, which creates an abstraction of continuity and ease-of-use for managing hard drive replacement, repartitioning and backup. (source: [[WikiPedia:Logical_Volume_Manager_(Linux)|WikiPedia]] ) |
Contents
Description
In Linux, Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a device mapper target that provides logical volume management for the Linux kernel. LVM is used for the following purposes:
- Creating single logical volumes of multiple physical volumes or entire hard disks (somewhat similar to RAID 0, but more similar to JBOD), allowing for dynamic volume resizing.
- Managing large hard disk farms by allowing disks to be added and replaced without downtime or service disruption, in combination with hot swapping.
- On small systems (like a desktop), instead of having to estimate at installation time how big a partition might need to be, LVM allows filesystems to be easily resized as needed.
- Performing consistent backups by taking snapshots of the logical volumes.
- Encrypting multiple physical partitions with one password.
LVM can be considered as a thin software layer on top of the hard disks and partitions, which creates an abstraction of continuity and ease-of-use for managing hard drive replacement, repartitioning and backup.
(source: WikiPedia )
Subitem 1.1
Text
for i in `ls`; do echo $i; done